Key Takeaways
- Productivity is a pivotal indicator of economic health, impacting business efficiency, profitability and competitive standing while influencing broader economic growth and living standards.
- Both consulting and accounting firms are increasingly focusing on providing more customized and agile services to meet evolving client expectations, leveraging data and analytics to align closely with client demands.
- Businesses must strategically manage productivity through technological investment and workforce training to adapt to fluctuating economic conditions, ensuring they remain resilient and competitive.
Over the past decade, businesses across the United States, United Kingdom and Australia have faced ongoing productivity challenges tied to economic uncertainties, rapid technology changes and shifts in workplace dynamics, accelerated by global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. Recent data underlines this reality: Labor productivity in the United Kingdom saw a slight 0.1% decline year-over-year, while Australian labor productivity dropped by 0.8% in the June 2024 quarter.
To thrive in this environment, understanding these productivity shifts is crucial for businesses. Recognizing these trends allows firms to proactively respond and implement strategies to mitigate adverse effects and leverage potential opportunities. As the global economic environment transforms, the capability of businesses to navigate and respond to these productivity challenges will be essential for sustainable growth and resilience.
What is productivity?
Productivity measures the effectiveness with which resources like labor and capital are used to generate goods and services, assessing how inputs are converted into outputs over time. For instance, labor productivity can be measured by units produced per hour of work, while capital productivity evaluates output from investments in technology and equipment.
Why productivity matters
For the economy
Beyond individual businesses, productivity is a core indicator of economic health, influencing growth, wages and living standards. Higher productivity enables economies to produce more with the same or fewer resources, ultimately boosting profitability and fueling demand for skilled labor. This growth drives wage increases and improves living standards, underscoring productivity’s central role in a thriving economy.
For businesses
Productivity’s impact extends to a business’s efficiency, profitability and competitive positioning, directly influencing its ability to optimize resource use and respond to market changes.
- Business efficiency: Enhanced productivity streamlines processes and maximizes resources. For instance, consulting firms leverage productivity gains through advanced project management and technology that expedite service delivery.
- Profitability: Increased productivity reduces input costs, boosting margins. Finance and accounting firms use productivity-focused tools to efficiently manage larger client portfolios with high accuracy, supporting profitability with less manual intervention.
- Competitiveness: In competitive markets, productivity allows firms to differentiate by offering superior services at a lower cost. Consulting firms known for quick project delivery and high client satisfaction can capture more market share and strengthen their reputation.
How do productivity trends impact business strategy?
Productivity trends emerging since the global financial crisis (GFC) and intensified by COVID-19 have introduced new layers of complexity for businesses. To navigate and capitalize on these dynamics, firms need to address both short- and long-term productivity challenges.
In the short term, fluctuations may lead to operational bottlenecks and cost pressures that compromise customer satisfaction. In the longer term, persistent productivity slumps might compel firms to rethink their strategies, increasing investments in technology and workforce upskilling to build resilience.
Post-GFC productivity challenges
As firms strive to sustain productivity in a fluctuating global economy, understanding the origins of today’s productivity trends is important. Patterns set in motion after the GFC have continued to shape productivity, posing ongoing challenges for economies like the United States, United Kingdom and Australia.
These economies have been grappling with stagnant productivity growth in the aftermath of the GFC, which has had significant implications for firms that rely on efficient resource use to maintain competitiveness.
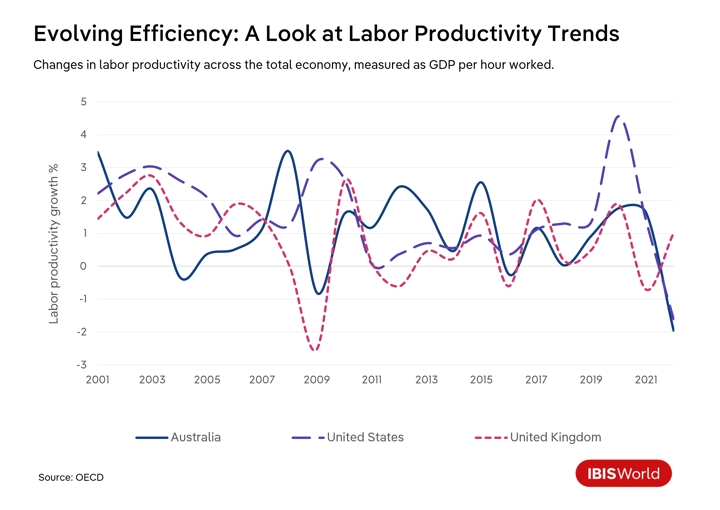 United States
United States
In the United States, the slowing pace of labor productivity growth became distinctly noticeable with the annual growth rate dropping from an average of approximately 2.2% in the early 2000s to 0.9% from 2010 to 2019. This downturn has mainly resulted from a slump in business investments, especially in innovative technologies, and labor market dynamics, which have seen low-productivity service jobs become more prevalent.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom has faced its own productivity puzzle, with productivity growth stagnating at a mere 0.3% annually from 2008 to 2019. The GFC particularly strained the financial sector, a cornerstone of the UK economy, contributing to the long-term drag on productivity. Underinvestment in crucial areas like infrastructure and workforce skills has exacerbated the issue.
Australia
Australia's scenario mirrors the patterns of the United Kingdom and the United States but brings unique challenges to the forefront. In the aftermath of the GFC, Australia navigated economic recovery, focusing on stimulating various sectors through fiscal measures. Even so, productivity growth was uneven, highlighting a reliance on mining. While effective in the short term, this strategy underlined the risks of dependence on a single sector and pointed towards the need for diversification.
The pace of technological adoption varied significantly among sectors, which inevitably influenced productivity trends. Financial and professional services quickly integrated new digital technologies, but sectors like manufacturing were slower in adopting digital advancements, contributing to lagging productivity.
COVID-19's productivity impact
While economies were already grappling with productivity stagnation in the years following the GFC, the COVID-19 pandemic introduced new layers of complexity. The shift to remote work had an immediate impact on productivity across Australia, the United Kingdom and the United States. Initially, this shift caused productivity drops as businesses and employees navigated new technologies and adapted to home-based work environments.
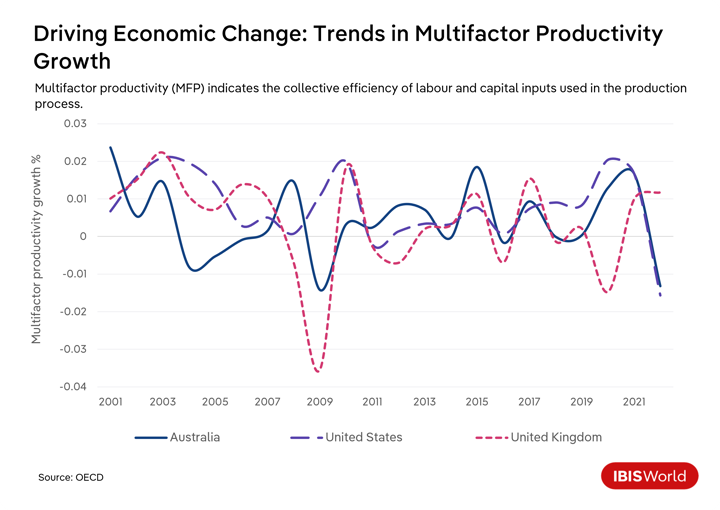 This shift also revealed significant variations in labor productivity across different sectors. Industries that require physical presence, like hospitality and retail, experienced severe layoffs. In contrast, service-based sectors were mostly able to maintain or even increase their output, skewing productivity.
This shift also revealed significant variations in labor productivity across different sectors. Industries that require physical presence, like hospitality and retail, experienced severe layoffs. In contrast, service-based sectors were mostly able to maintain or even increase their output, skewing productivity.
As firms downsized physical office spaces and trimmed administrative expenses, they inadvertently experienced gains by maintaining outputs with fewer employees. Even so, as pandemic restrictions eased, inflationary pressures intensified, reducing firms’ capacity to scale operations effectively. This trend, coupled with the challenge of managing expanding workforces post-restriction, led to slumps, notably in Australia and the United States.
How are productivity trends shaping industry strategies?
As the dust from COVID-19 settles, sectors like consulting, accounting and financial services are reshaping their strategies to adapt to productivity trends. Each sector has approached these challenges uniquely, integrating new technologies and adjusting operational models to improve their resilience and efficiency.
Consulting services
The impact of productivity trends on consulting services globally is significant. Technological advancements have allowed consulting firms to improve operational efficiency by automating routine tasks, using sophisticated project management tools and employing advanced data analytics. This transition has allowed consultants to focus on high-value tasks, strengthening firms' capacity to manage complex projects.
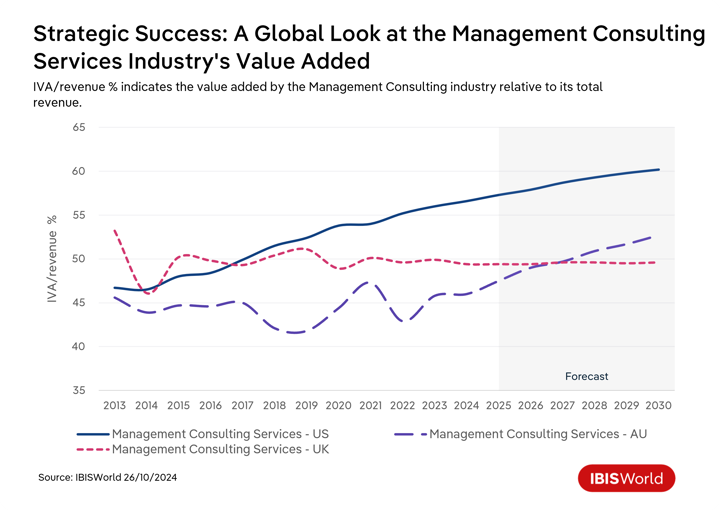 The adoption of remote and hybrid working arrangements post-pandemic is another key productivity trend influencing the consulting sector, reflecting a shift towards more flexible, decentralized work environments. This approach enhances access to a broader talent pool while promoting flexibility and job satisfaction, which are crucial to improving retention rates and reducing associated retraining costs. For instance, employees who can perform their work anywhere are 2.3 times more likely to stay with their company. Even so, consulting firms have needed to balance these trends with the benefits of in-person connectivity and collaboration in offices to maintain productivity and avoid employee burnout from working blurred hours from home.
The adoption of remote and hybrid working arrangements post-pandemic is another key productivity trend influencing the consulting sector, reflecting a shift towards more flexible, decentralized work environments. This approach enhances access to a broader talent pool while promoting flexibility and job satisfaction, which are crucial to improving retention rates and reducing associated retraining costs. For instance, employees who can perform their work anywhere are 2.3 times more likely to stay with their company. Even so, consulting firms have needed to balance these trends with the benefits of in-person connectivity and collaboration in offices to maintain productivity and avoid employee burnout from working blurred hours from home.
As consulting firms have looked to improve productivity, client expectations have also evolved to demand quicker and more tailored consulting services, forcing firms to adapt by refining their operations for greater responsiveness and customization. In response, firms are leveraging big data and advanced analytics to make informed, strategic decisions that align closely with client needs.
Tips for success
- Help clients identify workflow barriers: By conducting a thorough assessment of client workflows, consultants can pinpoint areas where processes slow down or where manual tasks hinder productivity. Offering actionable recommendations to streamline these workflows, like simplifying approval chains or automating basic administrative tasks, enables clients to focus on their core activities and respond faster to market demands, enhancing their operational flow and satisfaction.
- Provide scalable, modular services: Designing consulting packages that provide various levels of engagement allows clients to access increased support when productivity demands rise. This could include offering add-on services like temporary project management support or targeted workshops during high-demand periods. This adaptive model helps clients tackle productivity challenges as they arise without overhauling their entire strategy.
- Cross-project collaboration: Creating internal knowledge-sharing hubs or task-specific teams that can support multiple client projects simultaneously reduces setup and coordination time for each new engagement. By fostering a collaborative approach among consultants, firms can respond quickly to client needs, reduce project lead times and ensure consultants spend their time on value-adding work, all while maintaining efficiency across engagements.
Accounting services
Over the years, the accounting sector has demonstrated improvements in productivity, as shown by increasing revenue per employee across the United States, Australia and the United Kingdom. This improvement can be largely attributed to the strategic focus on technological integration and operational efficiencies, which have shifted the services offered.
Essential to this transformation is the widespread adoption of accounting management software, which has enhanced productivity by supporting remote workplaces and optimizing workflow. Climbing demand for diversified services amid an increasingly competitive market is also encouraging a more client-focused approach.
The adoption of cloud-based accounting software has been a game-changer, freeing up valuable time for accountants to focus on delivering value-added services like business advisory, which has seen a surge in demand post-pandemic. For example, BDO UK introduced a secure generative AI platform called Personas as part of its continuous investment in digital innovation. By leveraging the latest GPT-4 models, Personas is set to streamline daily tasks, allowing employees to focus more on providing complex, strategic advice that clients and businesses require.
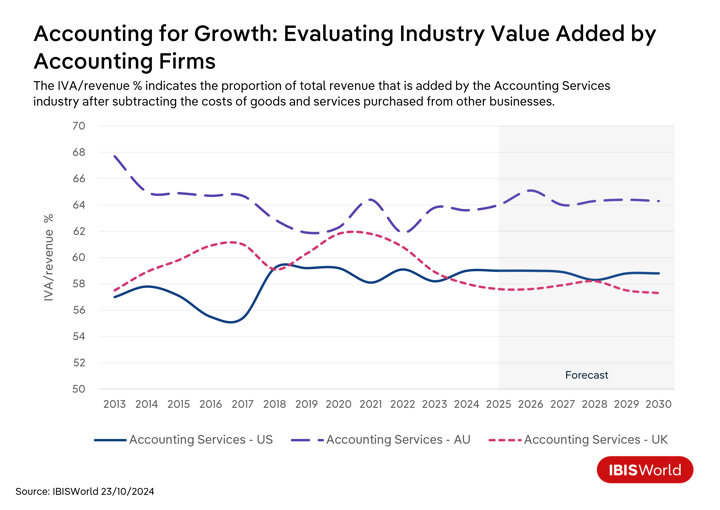 Australian accounting firms have leveraged this shift to boost their IVA/revenue ratio from 62.3% in 2019-20 to 64.0% in 2024-25. This rise reflects their strategic focus on offering high-value services in response to client needs, even as revenue per employee has temporarily dropped over the same period. This slump in revenue per employee indicates that accounting firms have continued to employ additional staff during this transition period to effectively implement these changes.
Australian accounting firms have leveraged this shift to boost their IVA/revenue ratio from 62.3% in 2019-20 to 64.0% in 2024-25. This rise reflects their strategic focus on offering high-value services in response to client needs, even as revenue per employee has temporarily dropped over the same period. This slump in revenue per employee indicates that accounting firms have continued to employ additional staff during this transition period to effectively implement these changes.
Accounting firms in the United Kingdom and United States have exhibited different trends compared to their Australian counterparts. A notable factor in these regions is persistent skill shortages, exacerbated by high demand for accounting services. This shortage has driven accounting firms to raise prices, increasing revenue per employee and encouraging a focus on capital investment rather than significant workforce expansion.
Firms are increasingly tapping into sophisticated technologies like big data analytics and automation tools, which address workforce gaps by reducing the reliance on manual labor. Although these strategies have successfully boosted revenue per employee, they have simultaneously led to a drop in IVA/revenue ratios over the five years through 2024-25.
Tips for success
- Efficient financial close processes: Many clients face time constraints and pressure at the end of each financial period. Accountants can assist by advising on streamlined closing processes that reduce manual entry, consolidate tasks and simplify reconciliation. By helping clients implement more efficient close routines, accounting firms enable them to achieve quicker, more accurate reporting, which in turn supports their productivity and decision-making.
- Support cash flow management: Cash flow challenges can often disrupt client productivity, especially during periods of slow revenue collection or high outgoing payments. Accountants can add value by setting up structured cash flow forecasts and advising on budgeting techniques that enable clients to anticipate and manage liquidity needs effectively. This proactive approach allows clients to maintain steady operations without interruptions, aligning financial stability with productivity.
- Document management automation: Within the firm, setting up a centralized, automated document management system can reduce time spent on retrieving, sharing and archiving essential client records. This organizational improvement enhances team productivity, allows for smoother client interactions and ensures that accountants have the information they need when they need it, reducing delays and improving overall service quality.
Financial services
Across the financial services sectors in the United States, United Kingdom and Australia, firms focus on labor productivity and multifactor productivity. Each region implements strategic measures that intertwine technological advancements, regulatory compliance and skilled employees, albeit in unique ways tailored to their economic landscapes. For instance, JP Morgan Chase & Co, with a vast workforce, used to dedicate 360,000 hours annually to routine tasks like interpreting loan agreements. The COIN (Contract Intelligence) program now completes these tasks in seconds using a machine learning system. This innovation boosts productivity and reduces errors.
The use of advanced technologies like AI, blockchain and data analytics has propelled productivity in the United States, setting a benchmark for automation and efficiency that directly boosts productivity. This trend in technological adoption is mirrored in Australia, where digital banking and automation have vastly expanded the capacity to handle transactions and client interactions without a proportional hike in labor input.
Despite facing productivity lag in response to Brexit-related market uncertainties, the UK financial sector is adopting similar technologies. UK firms are increasingly turning to fintech innovations and digital transformations to bridge the productivity gap with the United States. Despite these challenges, the City of London Corporation identifies financial and professional services as one of the most productive industries within the United Kingdom in 2023.
The regulatory landscape also influences each region's approach to improving productivity. Australia has advanced in using regulatory technology (RegTech) to streamline compliance processes. In contrast, the United Kingdom's financial firms are re-evaluating their compliance strategies in response to Brexit, turning towards technological solutions that can manage the evolving regulations.
Workforce development is essential in all three regions, focusing on continuous learning and skill-building to keep up with technology. There’s also a strong trend towards building a workforce skilled in data-driven decision-making, combining analytics with financial skills to support high productivity levels.
Tips for success
- Management during market volatility: Market volatility can strain client cash flow and disrupt planned expenditures, hampering their productivity. Financial service providers can assist clients by helping them structure more flexible financial arrangements or credit lines that provide liquidity during unstable periods. This support enables clients to keep operations running smoothly without productivity losses stemming from funding gaps.
- Compliance and reporting solutions: Regulatory demands often redirect client resources, eroding productivity by drawing staff attention away from core activities. Financial advisors can enhance client productivity by providing tailored compliance solutions that streamline reporting, automate regular filings and ensure clients can efficiently meet regulatory requirements. This frees up client time, allowing them to refocus on operational productivity.
- Workflow and collaboration tools: Financial firms can directly enhance their own productivity by adopting workflow automation and real-time collaboration tools that simplify team coordination and reduce administrative tasks. By streamlining operations internally, firms can respond to client needs faster and with greater precision, fostering client trust and satisfaction.
Final Word
Evolving productivity trends in key economies like the United States, Australia and the United Kingdom highlight businesses' need to understand and respond adeptly to fluctuations. These shifts demand agility and the adoption of innovative approaches alongside traditional methods.
Firms must embrace technological advancements and adapt to new operational norms, like flexible workplaces, to maintain competitiveness and efficiency. Balancing innovation with proven business practices is essential, allowing companies to leverage strengths while exploring new growth opportunities.
A commitment to continuous training ensures that firms can keep pace with technological progress and evolving market demands. By strategically navigating these productivity changes, firms enhance their resilience against immediate challenges and strengthen their positioning for future opportunities. This approach is crucial for sustaining growth.









